In the Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation reaction, ketones upon reaction with per-acids such as MCPBA or with H2O2 and a Lewis acid such as BF3 gives esters. The cyclic ketones upon similar treatment give lactones.
The ester or lactone formation is regiospecific and depends upon the migratory aptitude of the alkyl groups attached to the ketone carbonyl.
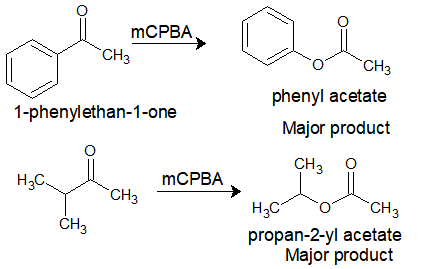
The migratory aptitude depends on how well it stabilizes the carbocation. So the migration can be predicted as in the order: tert. alkyl > cyclohexyl > sec. alkyl > phenyl > prim. alkyl > CH3
General reaction and mechanism:
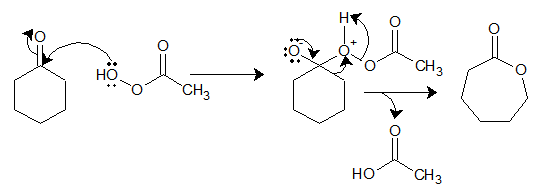
Per-acid oxygen attacks as a nucleophile to carbonyl carbon and then the alkyl group attached to carbonyl migrates to the attacking nucleophile while breaking O-O bond in the peracid to give ester from ketone.
Now let’s compare the products:
mCPBA: meta-chloroperbenzoic acid
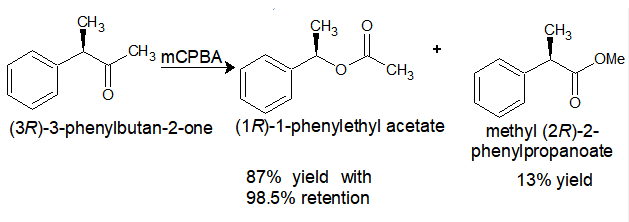
Stereochemistry: Retention in the stereochemistry is observed as a major product.
I hope you understood how to convert ketone to an ester using peracid! If you have any questions, ask on the home page!!
Dr. David McKinsey (OCT, Online educator)

